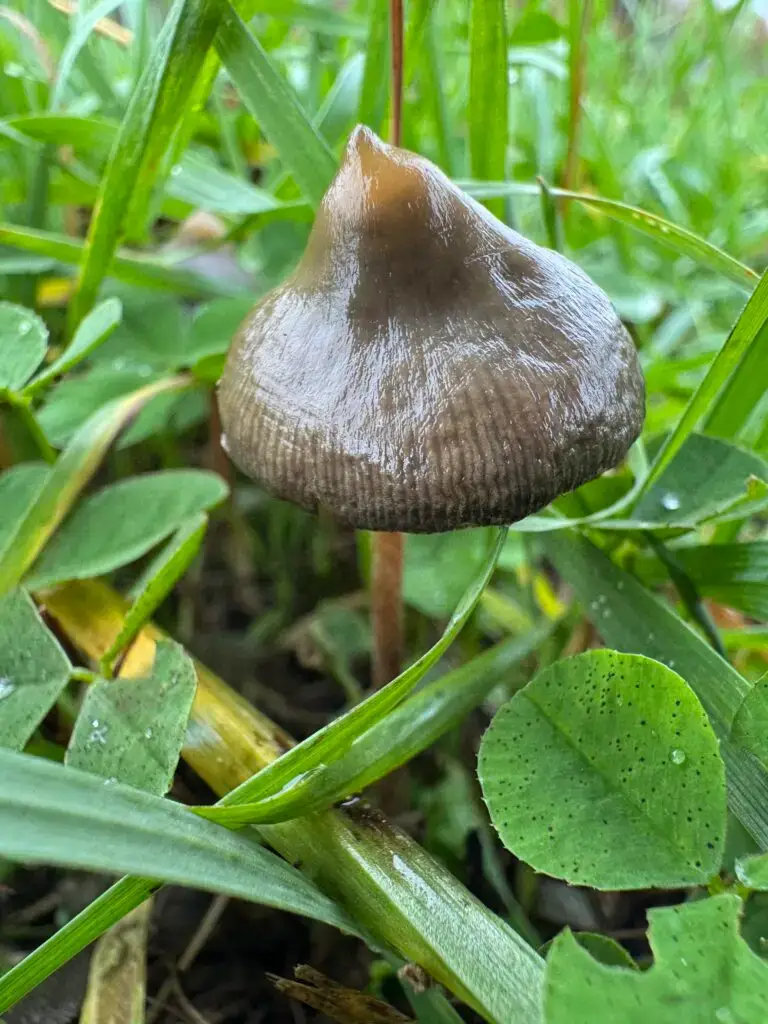

Psilocybe semilanceata: A Mycological Profile of the Liberty Cap Mushroom
Among all species in the Psilocybe genus, Psilocybe semilanceata, commonly


Psilocybe mushrooms, often referred to as “magic mushrooms,” have long been used for their psychoactive effects, primarily due to the compound psilocybin. Historically, these mushrooms have been used in religious and spiritual practices by indigenous cultures. In recent decades, however, there has been a growing interest in the potential therapeutic applications of psilocybin in the fields of medicine and psychology. This blog will explore the current state of psilocybe mushrooms in medical and psychological research, examining their potential benefits, the scientific evidence supporting their use, and the regulatory landscape surrounding these substances.
Psilocybe mushrooms have been used for centuries in various cultures, particularly in Mesoamerica, where they were consumed in religious ceremonies and healing rituals. The Western scientific community began to take an interest in these mushrooms in the mid-20th century. In 1957, R. Gordon Wasson‘s article “Seeking the Magic Mushroom” in Life magazine brought psilocybin to the attention of the general public. Subsequently, the Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann, who also discovered LSD, isolated psilocybin and psilocin from Psilocybe mushrooms in 1958.
Early research in the 1960s and 1970s explored the potential therapeutic benefits of psilocybin, but the increasing association of psychedelics with the counterculture movement led to their prohibition. The Controlled Substances Act of 1970 in the United States classified psilocybin as a Schedule I substance, severely restricting research and clinical use.
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in the therapeutic potential of psilocybin. Advances in neuroscience and a growing body of clinical evidence have prompted a reevaluation of psilocybin’s medical applications.
Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of psilocybin in treating a variety of mental health conditions. These studies have shown promising results, particularly in the following areas:

The therapeutic effects of psilocybin are believed to result from its interaction with serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor. This interaction leads to changes in brain connectivity and activity, promoting neural plasticity and facilitating new perspectives and insights. The altered state of consciousness induced by psilocybin allows individuals to process emotions and experiences in a unique and often transformative way.
Research using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has shown that psilocybin increases connectivity between different brain regions, particularly those involved in emotion regulation, self-reflection, and memory. This increased connectivity may help break down rigid patterns of thinking and behavior, allowing for new insights and emotional healing.
Psilocybin often induces mystical or peak experiences, characterized by a sense of unity, transcendence, and profound meaning. These experiences are strongly correlated with positive therapeutic outcomes, including lasting improvements in mood and well-being. The sense of interconnectedness and spiritual insight gained during these experiences can lead to lasting changes in perspective and behavior.

The regulatory landscape surrounding psilocybin is rapidly evolving. While psilocybin remains a Schedule I substance under federal law in the United States, several states and cities have taken steps toward decriminalization and legalization for therapeutic use.
The growing interest in psilocybin research and therapy presents both opportunities and challenges. As the field continues to evolve, several key areas warrant attention:
Ensuring the consistency and quality of psilocybin products is crucial for their safe and effective use in therapy. This includes developing standardized dosing protocols, rigorous quality control measures, and clear guidelines for practitioners.
Effective psilocybin therapy requires comprehensive support and integration services. This includes pre-treatment preparation, guided sessions with trained therapists, and post-treatment integration to help patients make sense of their experiences and apply insights to their daily lives.
As psilocybin moves toward wider acceptance and use, it is essential to address legal and ethical considerations. This includes ensuring equitable access to therapy, protecting patient privacy, and navigating the complex regulatory landscape.
Continued research is needed to further understand the mechanisms, benefits, and risks of psilocybin therapy. Additionally, educating healthcare providers, policymakers, and the public about the potential of psilocybin and other psychedelics is crucial for informed decision-making and acceptance.
The current state of psilocybe mushrooms in the medical and psychology fields is one of renewed interest and promise. With a growing body of evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of psilocybin, the future looks bright for its use in treating a range of mental health conditions. As research continues and regulatory landscapes evolve, psilocybin mushrooms may soon become an integral part of modern medicine and psychology, offering new hope for those suffering from depression, anxiety, PTSD, addiction, and other conditions.
The journey of psilocybin from ancient shamanistic practices to modern clinical research highlights its enduring significance and potential. As we move forward, it is essential to approach this powerful tool with respect, caution, and a commitment to rigorous scientific inquiry, ensuring that its benefits are maximized while minimizing potential risks. With the right frameworks in place, psilocybe mushrooms could revolutionize the way we understand and treat mental health, providing transformative experiences and lasting healing for countless individuals.

Among all species in the Psilocybe genus, Psilocybe semilanceata, commonly
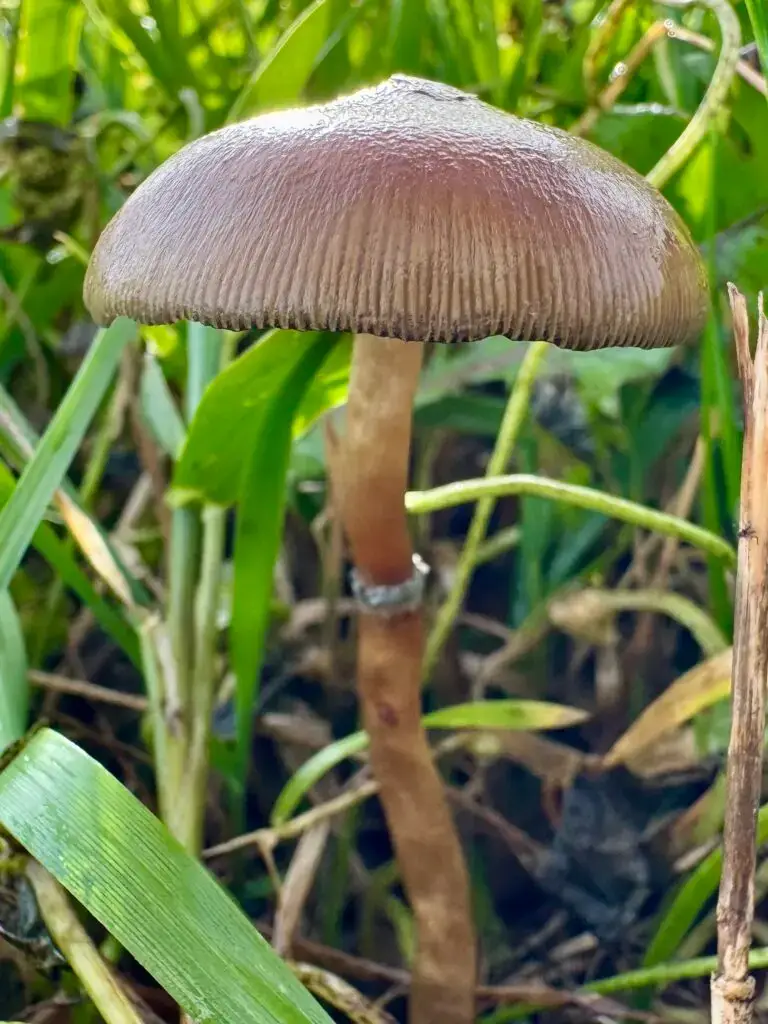

Among the many species studied within the Psilocybe genus, Psilocybe
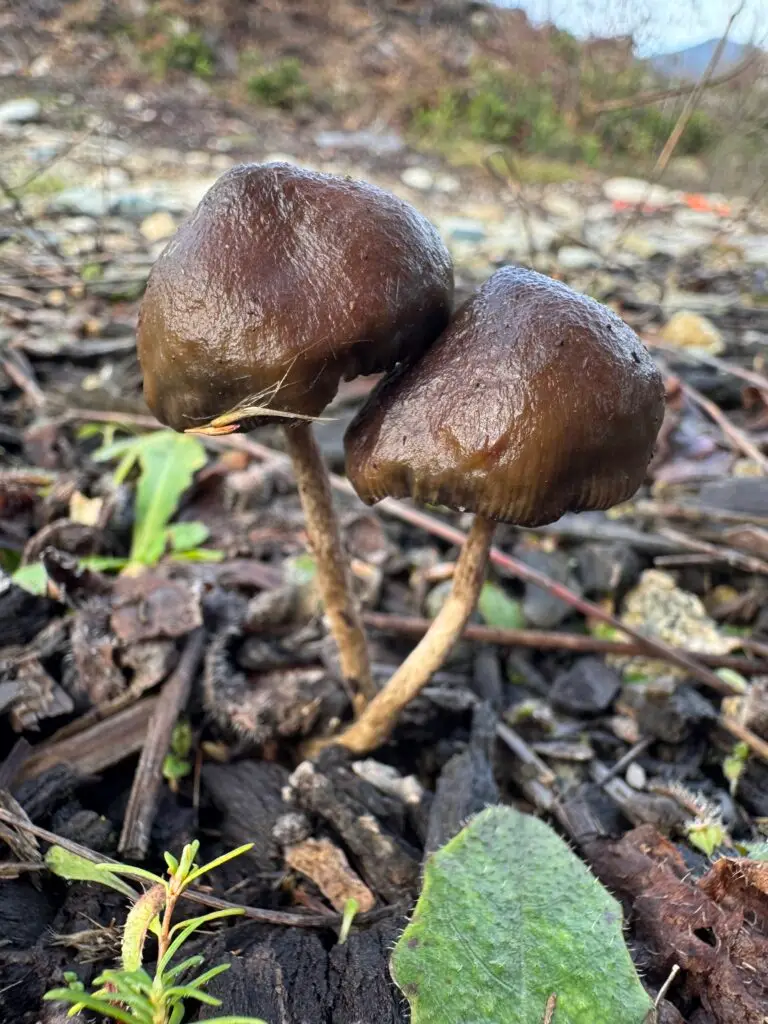

If you’re into mushroom microscopy, taxonomy, or the broader story

Microdosing Magic Mushrooms & Psilocybin: What’s Trending in 2025 In